When setting up email clients to connect to VPOP3, you need to know the IP address of your VPOP3 server. You should also make sure that the VPOP3 computer always has the same IP address.
Determining the VPOP3 computer's IP address for LAN access
Go to the Windows Control Panel on the VPOP3 computer and Network and Sharing Centre or View network status and tasks depending on how you are viewing the Control Panel icons.
Click on the text next to Connections. It often says Ethernet here, but the text could be different depending on your computer's configuration.
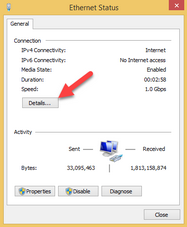
Press the Details button.
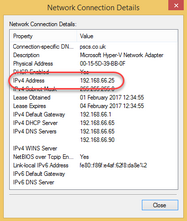
Look at the value of the IPv4 Address field. This is the IP address of the VPOP3 computer.
Determining the VPOP3 computer's IP address for access across the Internet
If you want to access VPOP3 from across the Internet, then you need to access it using the external IP address of your Internet connection.
If you have a static IP address from your Internet provider, then they should have told you your static IP address, or you can search for What is my IP address on an Internet search engine.
If you do not have a static IP address from your Internet provider, then you will either need to get one, or use a 'Dynamic DNS service' which will link a name to your dynamic IP address. The Dynamic DNS service you choose will help you set this up.
Once you know the IP address you need to set up VPOP3 and your router/firewall to allow access from outside your local network.
Fixing the VPOP3 computer's IP address on the LAN
For reliable operation, the VPOP3 computer's IP address should never change. Users' computers will be trying to access it on a certain IP address, and if the IP address changes, then the users' computers will not be able to contact it.
On most networks nowadays, computers obtain their IP addresses using a system called DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol). There will probably be a DHCP server on your network (eg a router or a network server), and when a computer/device is turned on, it asks that server for the network configuration, including which IP address it should use. If this is used, unchanged, on the computer running VPOP3, then it may mean that when the computer is restarted, it will have a different IP address, and users' computers will be unable to collect or send email.
So, you should make sure that the VPOP3 computer always has the same IP address. If you are in a business, then this is something that your network administrator should do, so if that is not you, you should coordinate with that person to avoid causing problems.
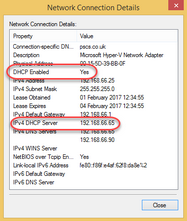
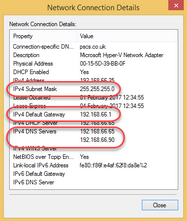
You can tell if your computers are using DHCP and where the DHCP server is by looking at the network status. If you follow the instructions above for finding the local network IP address, in the Details window, there will be information about the DHCP status.
In the above screenshot, this shows that this computer has received its IP address from a DHCP server (DHCP Enabled - Yes) and that the DHCP server used was at IP address 192.168.66.65 (IPv4 DHCP Server - 192.168.66.65).
Using DHCP reservation
The recommended way to fix the computer's IP address is to use something called 'DHCP reservation'. This tells the DHCP server that whenever it receives a request from a certain network adapter, then it should provide the same IP address. This means that a certain computer will always have the same IP address (unless the network adapter is changed).
How you do this depends on what DHCP server you are using.
Some instructions for common DHCP servers are below:
•Linux DHCPd - (example)
If your router is not shown above, then searching on the Internet for something like "<name of router> dhcp reservation" will probably find relevant instructions.
Using network settings
If you do not have a local DHCP server, then you can set the IP address manually. You can also do this if your DHCP server does not support reservations.
You must first choose a suitable IP address. This is a complicated subject, so we cannot include all possibilities. In a simple case, typically, it must be in the same subnet as the router, but be an address which is not used elsewhere. For instance, if your router is 192.168.1.1, and the subnet mask is 255.255.255.0, then your router's subnet has address 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.254. Choose an IP address in this range which is not used anywhere else. This can be hard to do if you do not have adequate network documentation...
If you have a DHCP server which does not support reservations, then you can probably use an IP address which is outside the DHCP server's "address pool" and which is not used by other fixed items such as your router.
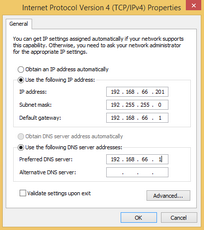
Once you have chosen the IP address to use you need to set it in Windows.
Go to the Windows Control Panel on the VPOP3 computer and Network and Sharing Centre or View network status and tasks depending on how you are viewing the Control Panel icons.
Click on the text next to Connections. It often says Ethernet here, but the text could be different depending on your computer's configuration.
Press the Properties button.
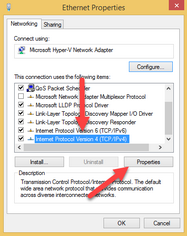
Select the Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) item, and press Properties.
Now, enter the details
Enter the chosen IP address in the IP address box.
The Subnet mask, Default gateway, and DNS servers can be discovered from the network details which can be obtained as described above.